Internal communication is the invisible nervous system of a company that ensures that everything runs smoothly. She is the link that ensures that everyone in the team is not only informed, but also committed. From the definition to the importance to the challenges – this article sheds light on the facets of internal communication strategies. We look at how digital and analog tools harmonize, how mistakes can be avoided and how success can be measured. With a practical view, enriched by concrete company examples, the article offers insights that every company can use to optimize its internal communication.
Definition of internal communication
According to the Gabler Business Dictionary, internal corporate communication describes a management task that supports the organization through targeted communication and behavioral measures. At an operational level, it includes the use of planned communication tools. Both in personal form and via media channels.
A distinction is made here:
- Structural internal communication along group, departmental or team structures
- Communication processes (direct or indirect, bilateral or multilateral)
- Communication flows such as top-down, bottom-up or horizontal
It also includes informal communication, i.e. unplanned conversations and the passing on of information, such as rumors or office grapevine.
Source: Gabler Wirtschaftslexikon – Internal communication
Differentiation from external communication.
While internal communication focuses on the exchange of information and knowledge within an organization, external communication is aimed at people and groups outside the company, including customers, business partners, investors, the media and the general public.
Both forms of communication are closely linked: Clear, consistent internal communication is a prerequisite for employees to represent the company authentically and uniformly to the outside world.
Types of internal communication
Internal communication can be categorized from different perspectives:
1. by direction
- Top-down: Information flows from the company management to the employees.
- Bottom-up: Feedback and ideas come from the employees to the management level.
- Horizontal: Exchange between colleagues or different departments.
2. by formality
- Formal: Planned, structured communication via defined channels (e.g. intranet, e-mail newsletter, team meetings).
- Informal: Spontaneous, unplanned exchange, e.g. personal conversations, chat messages or conversations during breaks.
3. by medium
- Analog: Face-to-face discussions, print media, notices.
- Digital: Emails, video conferences, employee apps, social intranet.
Internal communication in the company: Why it is more important today than ever
Internal communication is much more than just the flow of information between management and staff; it is a strategic success factor for every company. It creates a common understanding of goals and priorities, strengthens team cohesion and promotes an open corporate culture in which ideas, feedback and constructive dialog are a matter of course.
Particularly with regard to hybrid work, rapid market changes and digital transformation processes, well-functioning internal communication is the link that keeps everyone on the same level of knowledge and provides orientation. It ensures that employees are not only informed, but also actively involved and motivated.
A structured approach to internal corporate communication increases transparency, efficiency and commitment in the long term.
Measurably increase employee loyalty through communication
Transparent, respectful employee communication conveys security and trust. Employees who feel heard and included identify more strongly with the company and are more motivated to give their best. This has a direct impact on productivity and loyalty and also reduces staff turnover.

5 key factors for successful employee retention
Focus on strong employee retention: Increase productivity & reduce staff turnover with proven employee retention strategies.
Promoting corporate culture and conveying values
Corporate values only remain alive if they are communicated and exemplified in everyday life. Internal communication helps to convey these values and create a culture in which everyone pulls in the same direction. This is particularly important in growing or decentralized organizations where face-to-face encounters are becoming rarer.
Accelerating knowledge transfer and innovation
Open communication channels enable knowledge to be shared quickly, silos to be broken down and ideas to be developed further. Companies that actively promote internal exchange react more quickly to changes and develop innovative solutions. This is a decisive competitive advantage, especially in dynamic markets.
Goals of internal communication
For internal communication to be effective, it is not enough to simply disseminate information on a regular basis. It is crucial to clearly define the goal of each communication. Is the aim to provide guidance, support change or strengthen commitment? Without this clarity, measures remain arbitrary and their impact is difficult to measure.
In practice, the objectives of internal communication vary depending on the company situation, target group and phase. Information transfer, employee retention, cultural development and change support each place different demands on content, tone and channels.
The in-depth article “Internal communication objectives in detail” systematically examines these objectives. It shows what objectives internal communication can pursue, how they can be distinguished from one another, and how companies can tailor their communication measures to achieve them.

Goals of internal communication
Overview of internal communication goals: increasing engagement, sharing knowledge, supporting change, with practical examples and a checklist.
Challenges of internal communication
Internal communication does not work solely on the basis of good intentions or modern tools. In practice, it faces a number of structural and organisational challenges that have a significant impact on its success. Digitalisation, flexible working models and an increasing density of information are changing the way employees perceive and process information.
At the same time, demands for clarity, relevance and reliability are increasing. Different communication needs, hybrid working environments and a lack of personal contact increase the risk that information will be sent but not understood or accepted.
The following section presents the key challenges of internal communication and the most common mistakes that occur in this context. Concrete examples are used to show how these stumbling blocks arise and what measures companies can take to counter them in a targeted manner.

Challenges of internal communication
10 common mistakes in internal communication and how companies can avoid them, with practical tips for hybrid and digital working models.
Channels, formats & tools for internal communication
Once it is clear what goals internal communication is pursuing and what mistakes should be avoided, the focus shifts to operational implementation. It is not so much the individual content that determines success, but rather the question of how, in what form and with what tools communication takes place.
In practice, instruments, tools, channels and formats are often treated as synonymous. This lack of distinction leads to inefficient tool landscapes, redundant communication and excessive demands on employees. However, especially in complex organisations with hybrid working models, a clear communication architecture is crucial for conveying information in a targeted and comprehensible manner.
The in-depth article “Channels, formats and tools for internal communication” systematically classifies these terms. It shows how they differ from one another, how they interact effectively and what criteria companies should use to select and structure their communication tools.
Channels, tools and formats for internal communication
Which channels, formats and tools make internal communication effective? Structure, practical examples and checklist for companies.

Employee app and internal communication channels in comparison
Comparison of internal communication channels: analyse the pros and cons to find the best solutions for your company.
Internal communication KPIs: engagement, reach, relevance
Good internal communication is not only demonstrated by the publication of content or the use of modern tools. The decisive factor is whether messages are actually noticed, understood and lead to interaction or behaviour. Without measurable criteria, internal communication remains difficult to control and its contribution to the success of the company invisible.
Many organisations rely on subjective impressions or individual observations when evaluating their communications. As a result, potential for optimisation remains untapped and measures can hardly be compared or further developed. However, especially in complex communications landscapes with multiple channels, it is necessary to distinguish between impact and mere effort.
The in-depth article “Internal Communication KPIs: Engagement, Reach, Relevance” shows which metrics companies can use to measure the quality and effectiveness of their internal communication. It explains which KPIs are useful, how they are collected and how they can be used to continuously optimise content, formats and channels.
Internal communication KPIs: engagement, reach, relevance
Making internal communication measurable. Key KPIs for engagement, reach and relevance, including practical examples and a checklist.
Improve internal communication: 9 steps for companies
Many companies know that their internal communication could be improved, but the path from recognition to concrete implementation often remains unclear. Individual measures are introduced, new tools are tested or additional content is created without an overarching plan behind them. The result is selective improvements, but no lasting effect.
Effective internal communication does not result from individual actions, but from a systematic approach. It begins with an honest assessment of the current situation, defines clear goals and responsibilities, and develops a suitable channel and tool mix based on this. It is also crucial that measures do not remain static, but are regularly reviewed and further developed.
The in-depth article “Improving internal communication: 9 steps for companies” describes this process step by step. It provides practical examples of how organisations can analyse their internal communication in a structured manner, build it up in a targeted way and continuously optimise it, from the current analysis to the data-based KPI review.

Improve internal communication: 9 steps for companies
Improve internal communication in 9 steps. From analysis to goals to KPIs. Practical with examples, checklists and implementation tips.
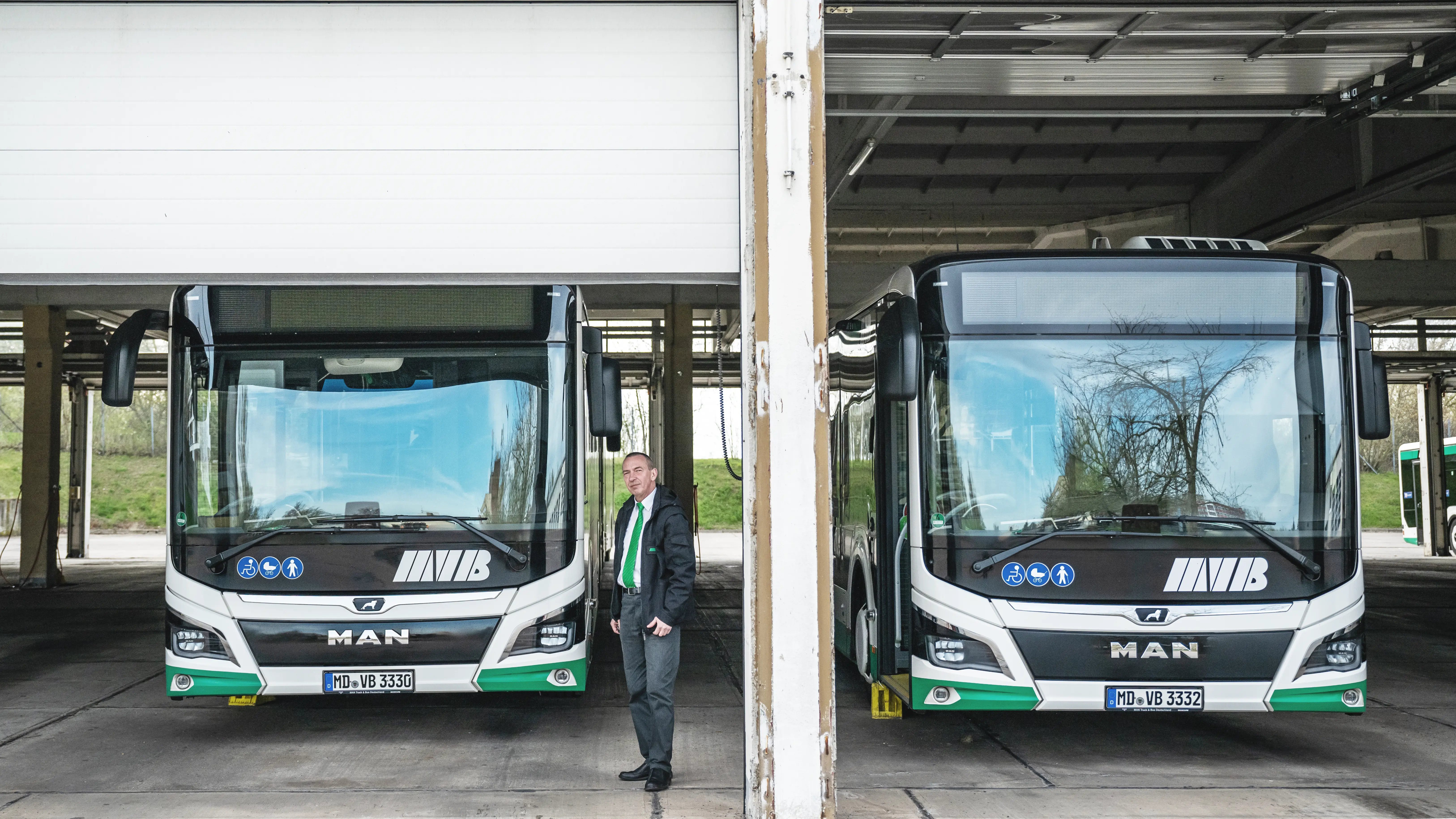

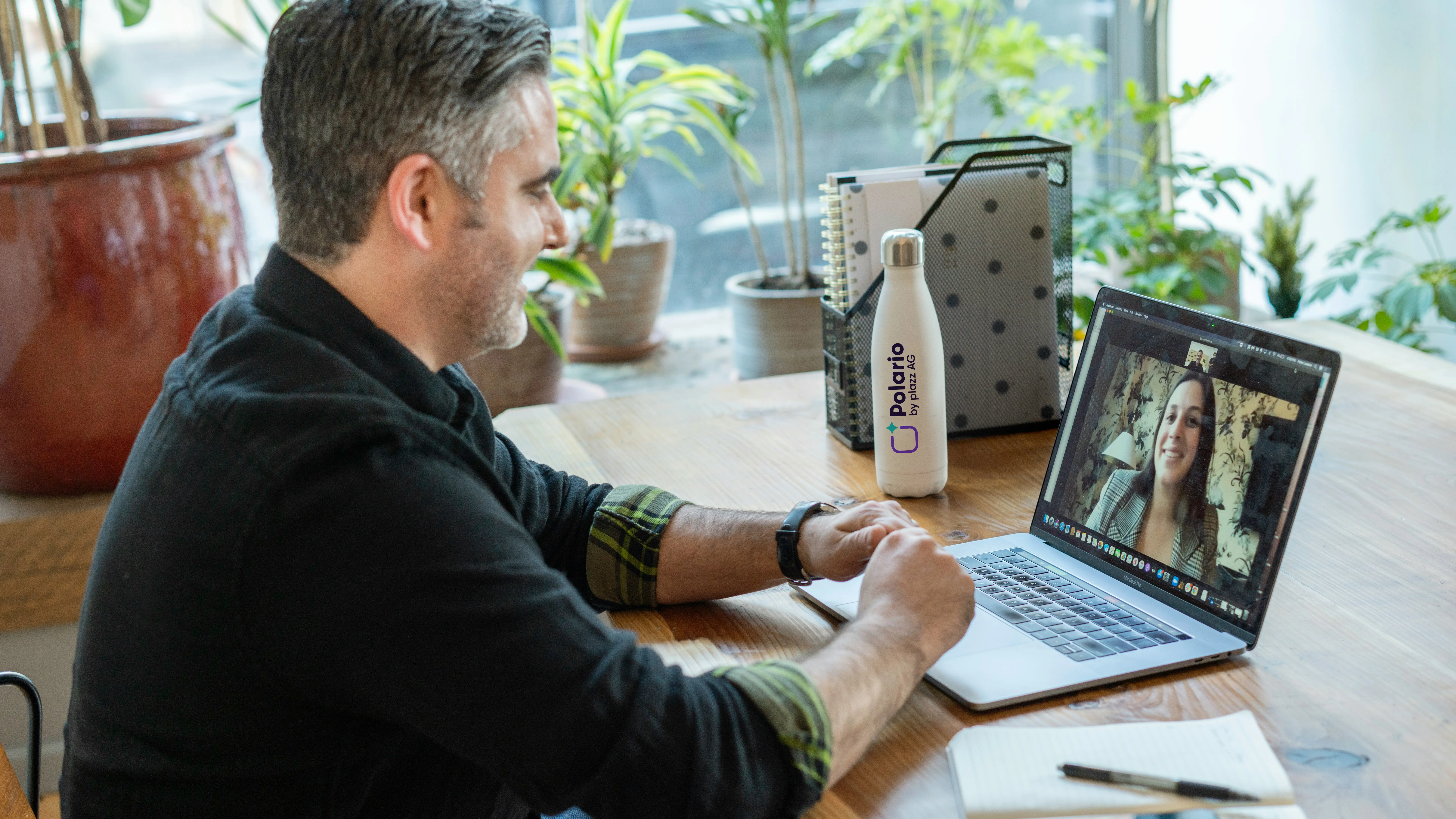
MVB Employee App
At Magdeburger Verkehrsbetriebe, Polario connects employees in real time, increases efficiency and saves time – digitally and sustainably!

OTLG Employee App – the digital success story
Learn more about contemporary employee communication for manufacturing-related companies, using the OTLG employee App as an example.
Digitising internal communication: Trends, Hybrid Work & AI
Today, internal communication is not only tasked with conveying information, but must also keep pace with the conditions of a digitalised working world. Hybrid working models, mobile target groups and rising expectations in terms of speed and personalisation are fundamentally changing how communication is organised and experienced.
Traditional, highly analogue communication approaches quickly reach their limits. They are often too slow, not sufficiently scalable and have limited reach, especially among non-desk workers. At the same time, digital platforms, automation and the use of artificial intelligence are creating new opportunities to make internal communication more efficient, relevant and measurable.
The in-depth article “Digitising internal communication: trends, hybrid work and AI” shows how companies can actively shape this change. It classifies current developments, explains the role of employee apps as a central interface and provides an outlook on how automation and AI will shape internal communication in the future.
Downloadable PDF checklist
Turn theory into practice: our checklist for better internal communication clearly summarises all the important steps from this guide, with clear to-dos that you can realise immediately.
🖇 Get your free PDF now and start optimising right away!
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What is internal communication?
Internal communication encompasses all planned and unplanned information and exchange processes within a company. This includes formal channels such as the intranet, employee apps and email, but also informal conversations between colleagues. The aim is to disseminate information efficiently, promote collaboration and strengthen a positive corporate culture.
What are the goals of internal communication?
The most important objectives are the rapid and reliable distribution of information, the promotion of transparency, the increase in employee commitment and satisfaction, the exchange of knowledge and the support of change processes. Good internal communication contributes directly to the company’s success.
What instruments are available?
The most common tools include digital tools such as email, chat programs, intranet, video conferences and employee apps as well as analogue formats such as notices, face-to-face meetings or company meetings. Each tool has its own strengths and the right choice depends on the target group, content and communication objective.
How can internal communication be improved?
Companies should regularly analyse the status quo, set clear goals and select suitable channels. It is important to establish an open feedback culture, prepare content for specific target groups and strategically plan the use of digital tools. Use the internal communication checklist as a starting point.
Are there examples of internal communication in regulated environments?
Magdeburger Verkehrsbetriebe (MVB) is a good example: before the introduction of an employee app, the flow of information between the transport service, control centre and administration was fragmented. Today, the app serves as a centralised, audit-friendly channel – with target group-specific push notifications (e.g. shift/safety updates), documented delivery/reading confirmation, roles and rights concept and a stored set of rules/documents. The result: faster, traceable communication, even for non-desk workers, and fewer coordination errors in shift operations.
You can find more information on this in our use case for the MVB employee app.





