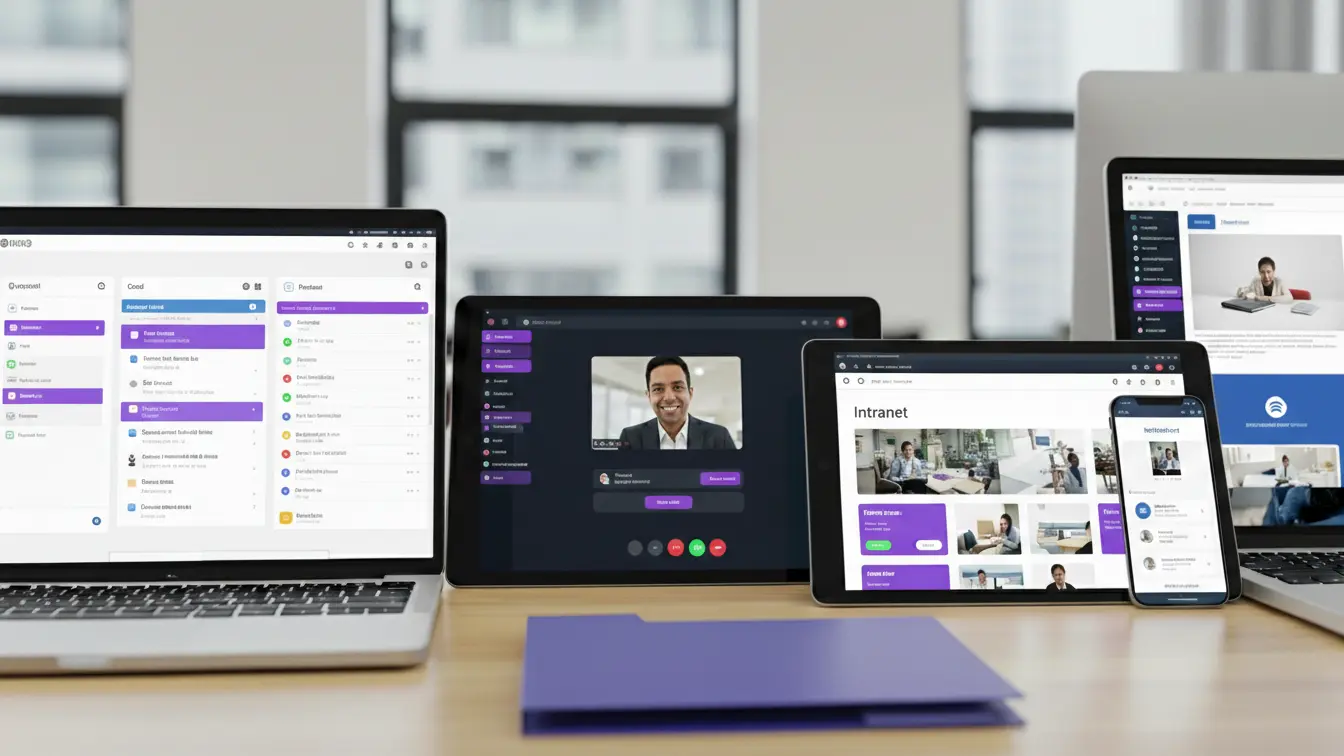
Internal communication only has a lasting effect if it is not viewed in isolation. The role it plays in the company, the goals it pursues and the challenges it faces are comprehensively classified in the article “Internal communication: definition, goals, instruments and practical examples“.

Internal communication: definition, goals, instruments & practical examples
Internal communication explained clearly. With goals, suitable channels and tools. Practical with KPIs, checklist and customer example.
In practical terms, however, a crucial question arises: how does content actually reach employees? Even clearly defined goals and well-prepared messages lose their impact if the channels are unsuitable, the formats are not appropriate for the target group, or the tools are used in an unstructured manner.
Im folgenden Beitrag stehen deshalb die Kanäle, Formate und Tools der internen Kommunikation im Mittelpunkt. Er schafft Klarheit darüber, wie sich diese Begriffe voneinander unterscheiden, wie sie sinnvoll zusammenspielen und nach welchen Kriterien Unternehmen ihre Kommunikationsarchitektur aufbauen sollten, um Informationen gezielt, verständlich und effizient zu vermitteln.
Channels, formats & tools for internal communication
Instruments, tools and channels in internal communication are three different elements that work together to form an effective communication strategy:
Instruments - The ‘what’ of internal communication
Tools are the methods and procedures used to disseminate information within the company or to promote the exchange of information. They determine what type of communication takes place. Examples include employee appraisals, internal newsletters, the intranet, team meetings and employee apps.
A good communication concept generally uses a mixture of synchronous and asynchronous tools to enable both rapid coordination and in-depth information distribution.
Tools - The ‘how’ of realisation
Tools are the specific technical or physical aids with which the selected instruments are realised. These include, for example, email programmes, chat tools such as Microsoft Teams or Slack, video conferencing solutions such as Zoom or Webex, as well as content management systems for the intranet. This also includes workflows for birthdays, shifts, safety messages = automated internal communication.
Choosing the right tools for internal communication depends on factors such as company size, IT infrastructure, security requirements and employees’ preferred way of working.
Channels - The ‘where’ of communication
Channels refer to the ways in which information is transported. This can be a physical location such as a notice board or meeting room, as well as a digital location such as a company chat, social intranet or employee app.
The choice of the right channel influences how quickly and comprehensively a message reaches its target audience.
Formats - The packaging of the message
Formats determine the way in which content is prepared and presented, regardless of the channel. These include text formats (articles, emails, blog posts), visual formats (infographics, photos), audiovisual formats (videos, podcasts) and interactive formats (surveys, live Q&As).
The format has a significant influence on how comprehensible, attractive and memorable a message is.
Why the distinction is important
The clear separation between instruments, tools, channels and formats helps companies to optimise their communication strategy in a targeted manner:
- It prevents overlaps and redundancies.
- It enables a customised selection of tools for the respective instruments.
- It ensures that messages reach the recipient in the right format via the right channel.
In large organisations in particular, this differentiation is crucial in order to efficiently organise the flow of information, make optimum use of resources and ensure a uniform line of communication.

Employee app and internal communication channels in comparison
Comparison of internal communication channels: analyse the pros and cons to find the best solutions for your company.
Instruments of internal communication
A variety of tools are used in internal communication, which can include both digital and analog formats:
Digital instruments
-
E-Mail
The classic digital communication tool. Emails are ideal for formal, documented communication, e.g. for announcements or minutes. Advantage: Anyone can read them, regardless of location. Disadvantage: If the frequency is too high, there is a risk of information overload and important content can get lost in the inbox.
-
Intranet
A central platform where employees can find company news, resources, guidelines and tools. Advantage: All relevant content in one place. Disadvantage: If the intranet is not regularly maintained, it quickly loses relevance and acceptance. A curated intranet is central to the exchange of knowledge within the company.
-
Social networks (internal)
Platforms such as Yammer or social intranet features promote a sense of community and cross-departmental dialogue. Advantage: Interaction and feedback are easily possible. Disadvantage: Requires active community moderation to ensure relevance.
-
Chat tools and messengers
Solutions such as Microsoft Teams or Slack enable fast, informal communication in real time. Advantage: High speed, simple group communication. Disadvantage: Can lead to constant availability and disrupt concentrated work.
-
Video conferencing systems
Tools such as Zoom or Webex are suitable for meetings, presentations and workshops across geographical borders. Advantage: Personal exchange despite distance. Disadvantage: Requires good technical equipment and can be tiring if there are too many meetings (‘Zoom fatigue’).
-
Employee Apps
Employee apps for internal communication often combine several tools in one solution, e.g. news feeds, chat, document storage and survey tools. Advantage: Mobile availability, personalised content, push notifications. Disadvantage: Requires initial introduction and training to ensure acceptance.
Analogue instruments
-
Notices and notice boards
A simple, cost-effective medium for general announcements and information. Advantage: Clearly visible to everyone on site. Disadvantage: Only effective for employees who are physically present.
-
Employee magazines and newspapers
Provide a periodic overview of company developments, projects and employee stories. Advantage: Long-lasting format with high value. Disadvantage: High production costs, low topicality with fast-moving topics.
-
Meetings and personal discussions
Direct, personal exchange, whether in a team meeting, in an office conversation or over coffee. Advantage: Immediate feedback, high level of commitment. Disadvantage: Time-consuming, not scalable for large groups.
-
Works meetings
A centralised format for sharing important company information with the entire workforce. Advantage: Everyone hears the same message directly from the company management. Disadvantage: Requires a great deal of organisational effort and is rarely possible spontaneously.
💡 Tip: The choice of tools depends heavily on the target group, message and desired form of interaction. Use a curated mix of tools: email, intranet, chat, video & employee app as core tools for internal communication.
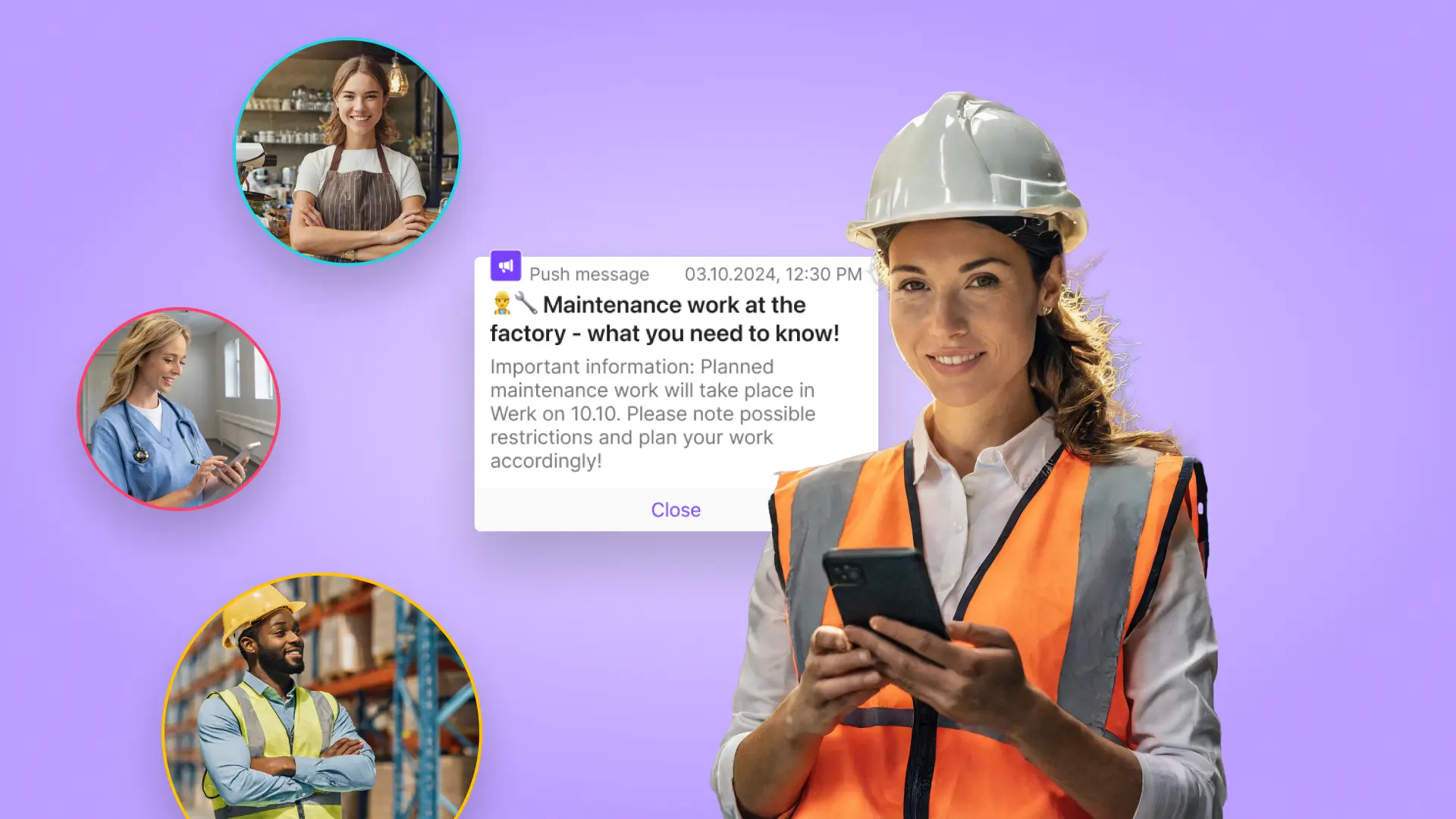
5 best practices for internal communication with frontline workers
Reach your frontline workers better! 5 smart best practices for fast, transparent & efficient internal communication.
Free checklist for effective internal communication
From analysis to implementation: this compact PDF helps you to structure internal communication in a targeted manner and initiate sustainable improvements.
✅ Concrete to-do lists instead of theory
✅ Immediately applicable for communication teams
✅ Suitable for operational and strategic managers
👉 Download now for free and optimise your internal communication step by step.